

If you haven’t found relief from your low back pain with conservative treatments, you are probably considering surgery. Once you decide on spine surgery, the most important decision you will face is whether to treat your back pain with artificial disc replacement or spinal fusion surgery. Each of the two options comes with certain benefits and certain risks and there are many different types of artificial disc replacement, so thoroughly understanding your options is the key to making this important decision.
Spinal fusion surgery is a surgical procedure to fuse the spinal bones together with a bone graft. There are many variations on this theme, but once the spine has healed, two or more vertebral bones will be fused together like a single bone.
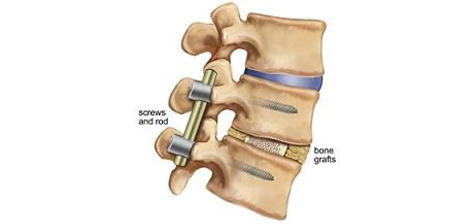
Artificial disc replacement surgery, on the other hand, is a surgical procedure to replace the problem vertebral disc or discs with a prosthesis or artificial joint.
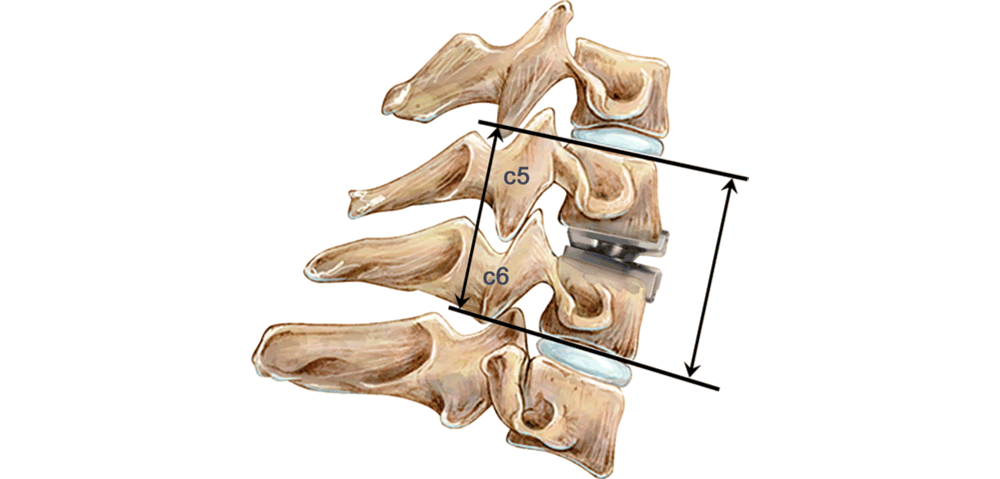
The main difference between disc replacement and spinal fusion is the mobility of the spine after the surgery. After fusion surgery, the treated area is less flexible and mobile because the vertebral bones of the spine no longer move independently. After disc replacement surgery, the prosthesis mimics the natural joint, so the spine is able to bend, flex, and rotate as it did when the disc was healthy.
Both types of back pain surgery can reduce or eliminate pain for most people. So, for people who are candidates for both surgeries, the choice between spinal fusion surgery or artificial disc replacement comes down to risks and benefits. Over the short and medium term, the success rates and complication rates between replacement and fusion are similar—success rates are relatively high and complication rates are relatively low.
Both procedures come with some risk of reoperation. The bones may not fuse after spinal fusion surgery, so a second procedure is needed. In some cases, people will need more levels fused later in life. For those who choose disc replacement, patients may need to have their artificial joint replaced in 40+ years, or even longer.
Artificial disc replacement offers some advantages over spinal fusion. The biggest advantage is that disc replacement preserves motion and mobility in the spine while fusion does not. This is especially important for people who want to live active and not just pain-free lives. In addition, recovery times after disc replacement are faster because the bones do not need to knit together, which takes time. Lastly, patient satisfaction ratings after both procedures are good, but people who have artificial disc replacement report greater satisfaction than those who had spinal fusion.
Here is a side-by-side comparison of the differences between having artificial disc replacement and spinal fusion surgery.
Spinal Fusion SurgeryArtificial Disc Replacement
| Reduces Pain | Yes | Yes |
| Preserves Mobility | Poor | Excellent |
| Recovery Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Risk of Reoperation | Low to Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Complication Rate | Low | Low |
| Patient Satisfaction | High | Very High |
| Reduces Disability | Yes | Yes |
Because spinal fusion and disc replacement provide excellent pain relief for most patients with chronic back pain, the choice is based on outcomes. Patients who opt for replacement tend to be more satisfied with their back pain surgery than those who choose fusion. This is mostly because patients who undergo replacement have much greater movement in their spines than those who had fusions. Remember that artificial disc replacement and spinal fusion are not for everyone. Your personal outcome depends on your unique clinical situation and the skill and experience of your spine surgeon. That is why you should choose a qualified spine surgeon who has extensive experience in both spinal fusion surgery and artificial disc replacement.